AI Newsletter - October 2024
1. Impact of Quantization on Large Language Models
Recent extensive testing of the Llama 3.1 series models has shed light on the critical role of quantization in optimizing LLM deployments. The evaluation, conducted across various model sizes (8B, 70B, and 405B), compared three quantization schemes against the baseline 16-bit model:
- W8A8-INT: 8-bit integer quantization for weights and activations
- W8A8-FP: 8-bit floating-point quantization for weights and activations
- W4A16-INT: 4-bit integer quantization for weights, 16-bit precision for activations
Key findings include:
W8A8 schemes (both INT and FP) achieved ~2x model size compression and 1.8x performance speedup in multi-request scenarios.
W4A16-INT provided ~3.5x model size compression and 2.4x speedup for single-stream scenarios, making it ideal for latency-critical applications.
Larger models (70B, 405B) showed negligible performance degradation post-quantization as shown in the following figures:
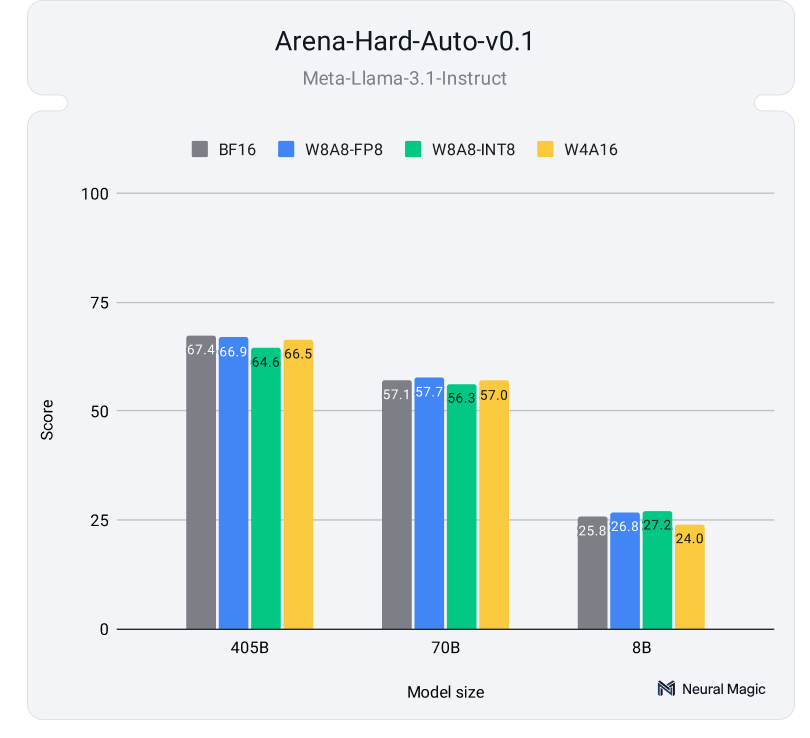
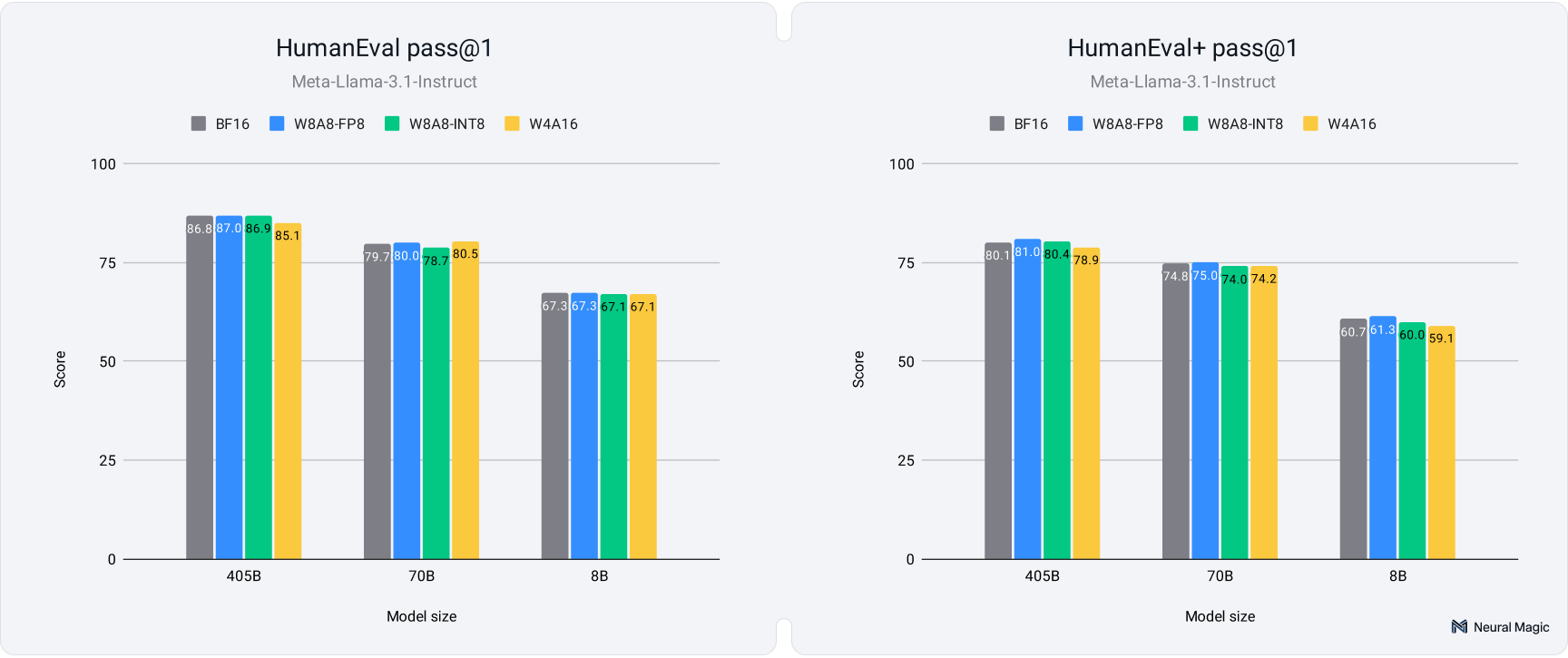
Smaller models (8B) experienced slight variability but maintained core semantic meaning and structural coherence as shown in the hard benchmarks above.
These results demonstrate that quantized models can maintain accuracy and quality compared to full-precision counterparts, offering significant computational savings and faster inference speeds. This makes quantization an essential tool for optimizing LLMs in real-world deployments, especially in resource-constrained environments or high-throughput scenarios.
2. PyTorch 2.5 Release Highlights
PyTorch 2.5 brings several significant improvements and new features to the popular deep learning framework. Key highlights include:
CuDNN backend for SDPA: This new backend for scaled dot product attention can provide up to 75% speed-up over FlashAttentionV2 on NVIDIA H100 GPUs, enabled by default for SDPA on H100 or newer GPUs.
Regional compilation for torch.compile: This feature allows compiling repeated nn.Modules (e.g., transformer layers in LLMs) without recompilations, reducing compilation latencies with only a 1-5% performance trade-off compared to full model compilation.
TorchInductor CPU backend optimization: Advancements include CPP backend code generation, FX fusions with customized CPU kernels, and support for vectorization of common data types and all Inductor IR operations. It’s compatible with both Linux and Windows, supporting Python and CPP wrappers, and AOT-Inductor mode.
FlexAttention (Prototype): A flexible API for implementing various attention mechanisms, leveraging torch.compile to generate fused FlashAttention kernels, eliminating extra memory allocation and achieving performance comparable to handwritten implementations.
Compiled Autograd (Prototype): An extension to the PT2 stack allowing capture of the entire backward pass, deferred until backward execution time, making it resilient to forward pass graph breaks.
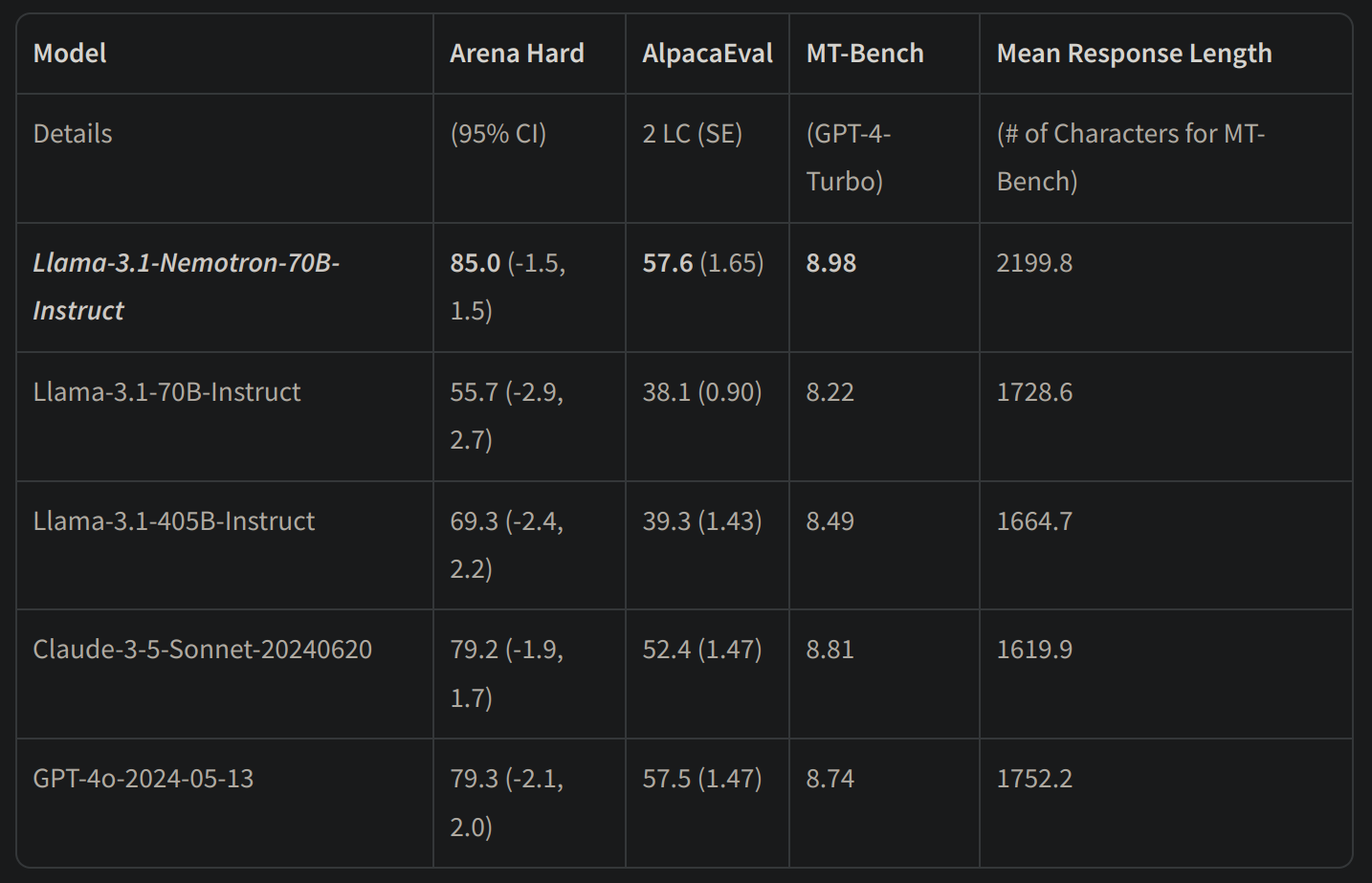
3. Nvidia’s Nemotron-70B Model Release
Nvidia has released Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct, a large language model specifically customized to enhance the helpfulness of LLM-generated responses to user queries. This model represents a significant advancement in the field of natural language processing and generation.
Key performance metrics:
- Arena Hard score: 85.0
- AlpacaEval 2 LC: 57.6
- GPT-4-Turbo MT-Bench: 8.98
As of October 1, 2024, Nemotron-70B claims the top position across all three automatic alignment benchmarks, surpassing formidable models like GPT-4o and Claude 3.5 Sonnet.
Training methodology:
- Base model: Llama-3.1-70B-Instruct
- Fine-tuning: RLHF (specifically REINFORCE)
- Reward model: Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Reward
- Training data: HelpSteer2-Preference prompts
The model demonstrates improved reasoning capabilities, evidenced by its ability to correctly answer questions like “How many r in strawberry?” without specialized prompting or additional reasoning tokens.
Nvidia has also provided a model conversion to the HuggingFace Transformers format (Llama-3.1-Nemotron-70B-Instruct-HF) and offers hosted inference with an OpenAI-compatible API interface at build.nvidia.com.
This release underscores Nvidia’s commitment to pushing the boundaries of LLM performance and usability, potentially reshaping the landscape of AI-powered natural language understanding and generation.
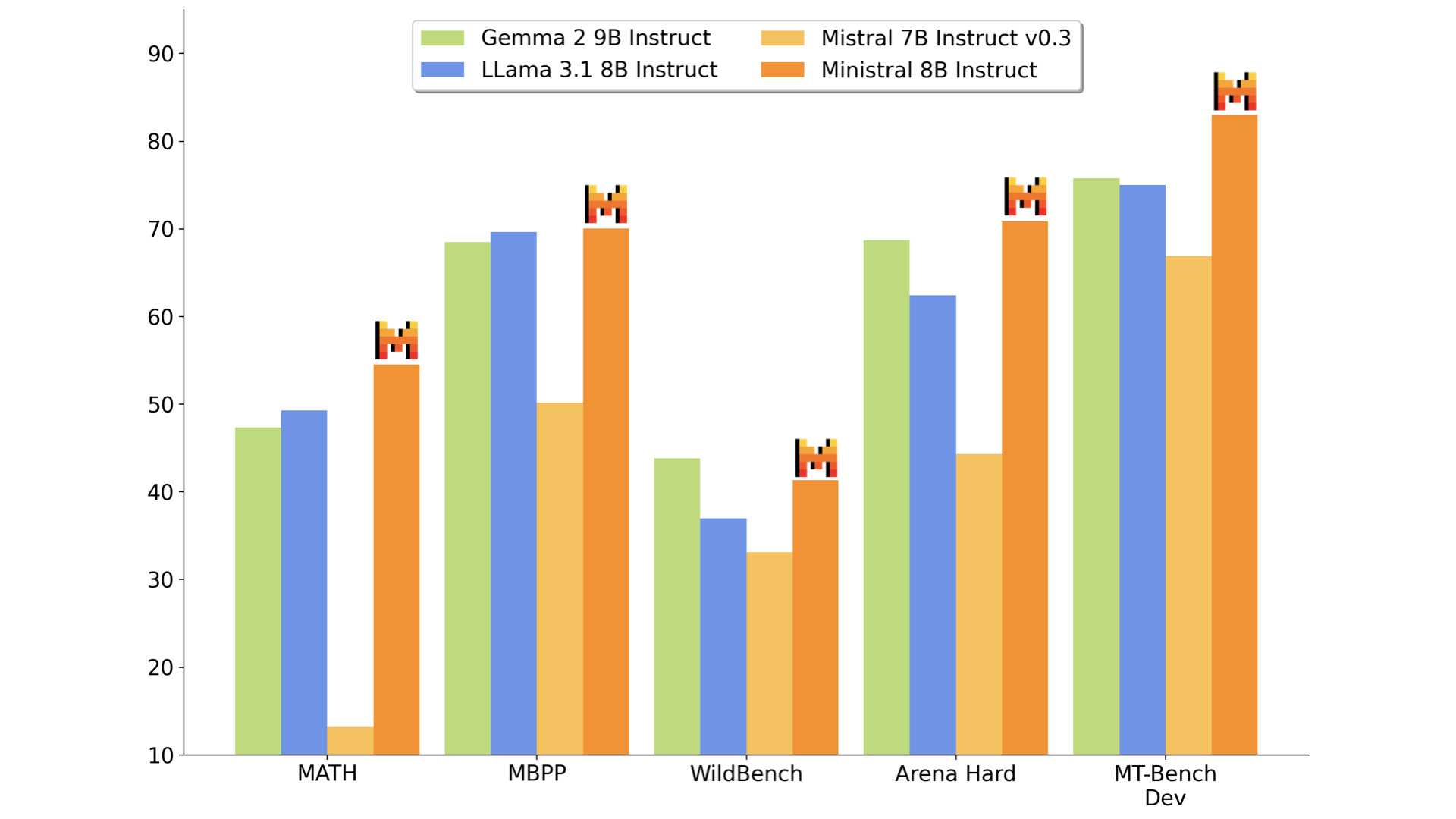
4. Ministral Models: Advancements in Edge Computing from Mistral AI
Mistral AI has introduced two new state-of-the-art models for on-device computing and edge use cases: Ministral 3B and Ministral 8B, collectively known as “les Ministraux.” These models mark a significant advancement in the sub-10B category, offering impressive capabilities in knowledge, commonsense reasoning, and function-calling.
Key features:
- Support for up to 128k context length (currently 32k on vLLM)
- Ministral 8B features a special interleaved sliding-window attention pattern for faster and memory-efficient inference
These models are designed to be versatile, suitable for various applications from orchestrating agentic workflows to creating specialist task workers. Their compact size and efficiency make them particularly valuable for edge computing scenarios where computational resources may be limited.
The release of les Ministraux on the first anniversary of Mistral 7B’s debut underscores the rapid pace of innovation in edge AI, potentially democratizing access to powerful language models for a wide range of devices and applications.
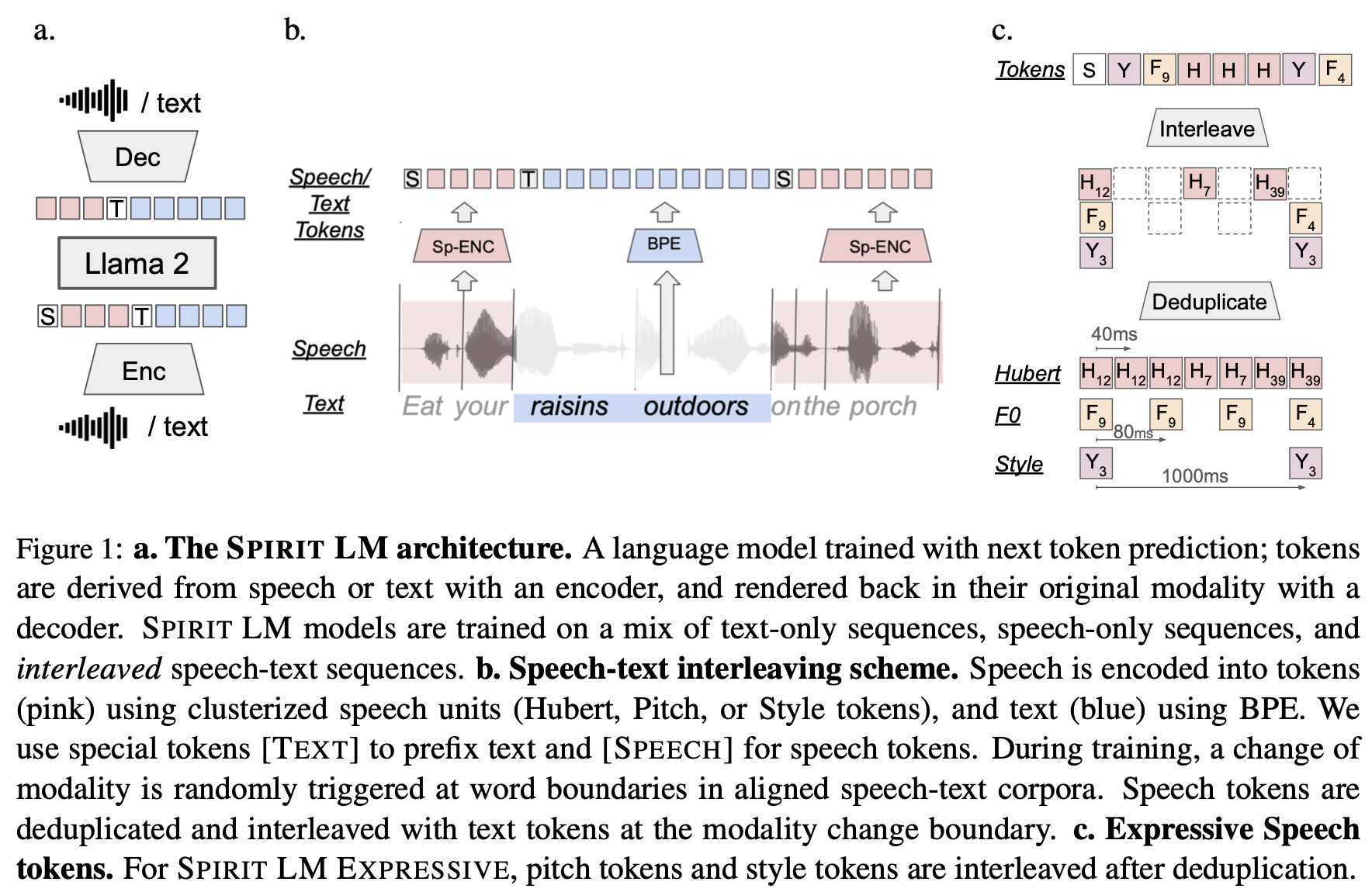
5. Spirit LM: Bridging Text and Speech in Language Models
Spirit LM represents a groundbreaking approach to multimodal language modeling, seamlessly integrating text and speech capabilities. Based on a 7B pretrained text language model, Spirit LM extends its functionality to the speech domain through continuous training on both text and speech units.
Key features:
- Unified token stream: Speech and text sequences are concatenated into a single stream of tokens.
- Word-level interleaving: Training utilizes a word-level interleaving method with an automatically-curated speech-text parallel corpus.
- Two versions:
- Base: Uses speech phonetic units (HuBERT)
- Expressive: Incorporates pitch and style units for enhanced expressivity
Spirit LM demonstrates both the semantic prowess of text models and the expressive capabilities of speech models. Notably, it exhibits few-shot learning capabilities across modalities, including Automatic Speech Recognition (ASR), Text-to-Speech (TTS), and Speech Classification.
This innovation opens up new possibilities for more natural and expressive human-computer interactions, potentially revolutionizing applications in voice assistants, accessibility technologies, and multimedia content creation.